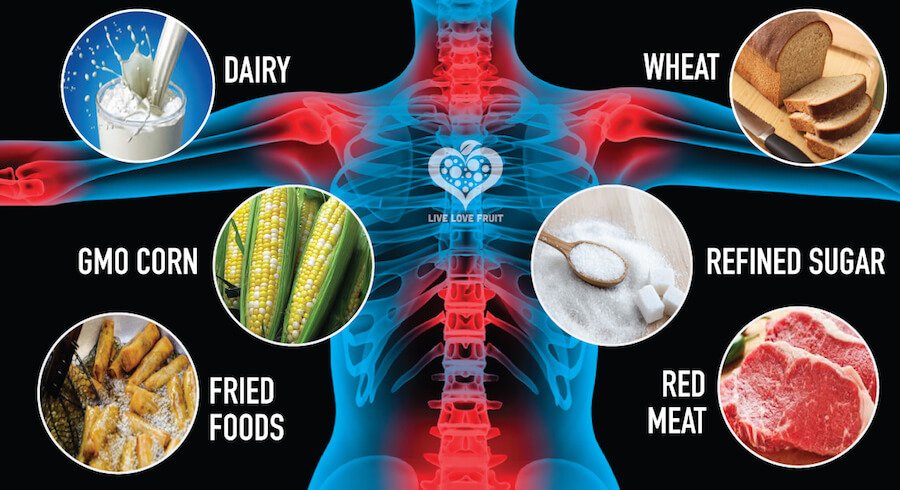
Did you know that some of the foods you consume trigger a less-than-favorable immune response in the body?
Unfortunately, many foods found in grocery stores today are made from ingredients the body doesn’t recognize. When our body doesn’t recognize a food particle, it goes into minor shock, triggering a cascade of inflammatory responses in the body.
Not all inflammation is bad, mind you. So let’s take a look at what inflammation is, and the different types that can cause long-term harm to the body.
What is Inflammation?
Inflammation is a natural response of our immune system to injury or infection. It is a complex process that involves various cells, tissues, and molecular signals. While inflammation is necessary for our body to heal and fight off infections, chronic inflammation can lead to various health problems.
Our bodies naturally inflame when the body is injured or ill. This is called acute inflammation.
Acute inflammation may manifest as swelling, redness, heat, as well as pain, and discomfort. Like when you stub your toe, that immediate pain you feel is the body working in action to help fix whatever just happened. It is a normal and effective response that facilitates healing.
Unfortunately, chronic inflammation is a different story.
Chronic inflammation is largely caused by poor diet, stress, lack of exercise, smoking, pollution, and lack of sleep. It is often seen in those with leaky gut syndrome, arthritis, fibromyalgia, celiac disease, and irritable bowel disease. It can also play a part in asthma and diabetes where the body continuously tries to heal tissues but fails.
As for weight gain and its connection to inflammation, inflammation makes our weight control hormone (leptin) to be less effective, which therefore causes weight gain. Thus, the two often come hand in hand.
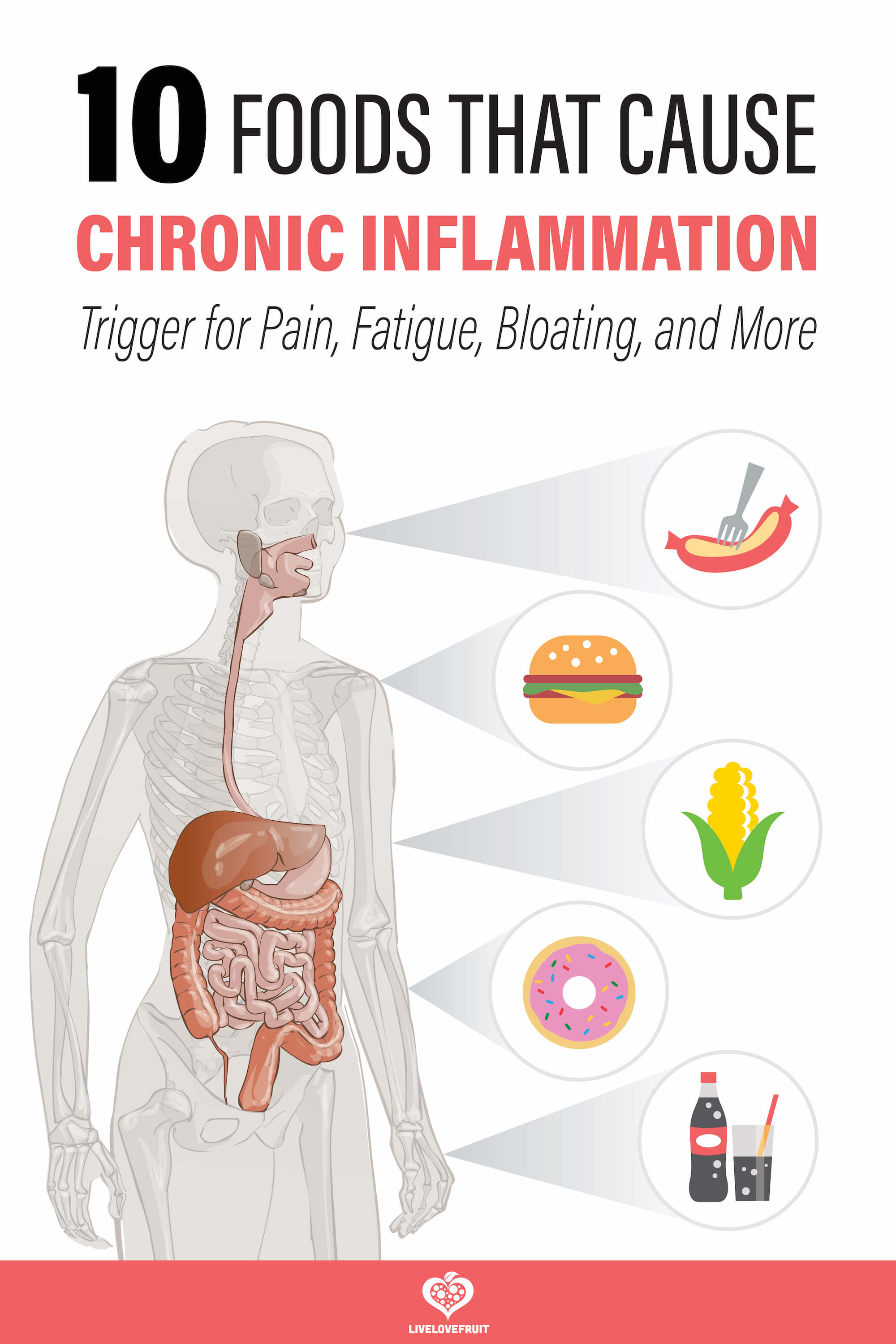
In this article, I will discuss the main foods that are known to cause inflammation and also provide information on the foods that can be included in your diet to help reduce it.
10 Foods That Cause Inflammation
One factor that can contribute to chronic inflammation is the food we eat. Certain foods can trigger an inflammatory response in the body, while others can help to reduce inflammation.
One of the first, and worst offenders is refined sugar.
1. Refined Sugar
Sugar, found in soda, baked sweets, candy, and snack bars, all increase glucose levels in our bodies, which we often cannot process quickly enough. This increases levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the body, increasing levels of inflammation in the body.
Studies have reported that sugar consumption in the diet causes inflammatory processes to become more active in humans. Dietary sugar promotes de novo synthesis of free fatty acids (FFA) in the liver (1✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source, which according to the lipotoxicity theory, would produce FFA metabolites that may trigger inflammatory processes and reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation (2✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
Sugar also suppresses the immune system, making your body more susceptible to diseases and infection (3✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
Satisfy your body’s natural need for glucose by eating fresh, ripe organic fruit, or opting for natural sugar sources that are rich in alkalizing minerals like maple syrup, coconut sugar, and yacon syrup.
2. Vegetable Oil
Vegetable oils from corn, canola, soybean, and safflower and all the products that contain them (yes, even vegan items like “butter” spreads), are high in omega-6 fats (the bad ones, not the good ones like those found in evening primrose oil).
The body needs a healthy balance of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids, but many people currently consume more 6’s than 3’s. This imbalance can contribute to chronic inflammation.
Currently, the Western diet provides a 6 to 3 ratio between 10:1 and 50:1 (4✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
Excess consumption of omega-6s can trigger the body to produce pro-inflammatory chemicals. And while omega-3s are anti-inflammatory, scientists have hypothesized that eating too much omega-6 counteracts these beneficial effects (5✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
So a diet with a lot of omega-6 and not much omega-3 will increase inflammation, while a diet high in omega-3s and low in omega-6 will reduce inflammation. Making sure these levels are in check is a crucial step in fighting inflammation.
Instead of vegetable oils, opt for healthier, anti-inflammatory oils like avocado, coconut, olive, and sesame oil.
3. Dairy Products
All dairy products are high in saturated fats, which are naturally inflammation-causing.
Large observational studies have shown direct associations between plasma saturated fatty acid status with markers of low-grade inflammation in both overweight and lean adults (7✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source, and children (8✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
In addition, as summarized in a recent review, activation of numerous genes related to inflammatory pathways has been documented in a number of clinical trials in humans following the consumption of saturated fatty acids (9✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
Dairy products contain lactose and casein proteins, both common allergens. When an allergen interacts with the immune system, it promotes the release of inflammatory neuropeptides, thereby triggering a cascade of unfavorable reactions in the body (10✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
There are plenty of dairy product alternatives out there such as plant-based milk, cheese, yogurt, and ice cream. For example, oat milk, almond milk, coconut milk, and cashew milk.
4. Wheat, Rye, and Barley
These wheat-containing grains all contain a common allergen – gluten.
When gluten enters the body, particularly in gluten-sensitive people, it responds by firing up the immune system and setting off an inflammatory cascade (11✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
The resulting effects of gluten sensitivity range from body pain to mucus production (runny nose, coughing up mucus), and tiredness.
According to gastroenterologist Alessio Fasano of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, “No human being completely digests gluten.” And for those who are gluten-sensitive, “undigested gluten triggers the release of zonulin” (12).
Zonulin is a protein that helps to regulate the “leakiness” of the gut. It’s responsible for opening and closing the spaces, known as the intestinal tight junctions (“tight junctions”), between the cells lining the digestive tract. Gluten just so happens to trigger the release of zonulin in Celiac patients, as well as those who are gluten-sensitive.
When our gut becomes leaky, a host of health problems can result. Instead of keeping undigested food particles safely in one place for excretion, these particles leak into the bloodstream and trigger body-wide inflammation (13✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
5. Fried Foods
Fried foods are another major trigger for inflammation, which can become chronic if consumed daily.
Fried foods contain high levels of inflammatory advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which are formed when anything is cooked to high temperatures, smoked, dried, fried, pasteurized, or grilled (14✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
One study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that consuming fried foods was associated with higher levels of CRP, a marker of inflammation, in both men and women (15✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source. Another study published in the Journal of Nutrition found that a diet high in fried foods led to increased levels of IL-6, another marker of inflammation, in healthy young adults (16✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
6. Refined Flour
Refined flour, in other words, anything that is white and not whole-wheat, has been stripped of slow-digesting fibers and nutrients, which means your body breaks down these items very quickly. This will spike insulin levels, resulting in a pro-inflammatory body response (17✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
One study published in the Journal of Nutrition found that a diet high in refined grains, such as white bread and pasta, was associated with higher levels of CRP, a marker of inflammation, in women (18✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source. Another study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that consuming refined grains was associated with higher levels of inflammatory markers, such as TNF-alpha and IL-6, in men (19✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
Furthermore, refined flour lacks the fiber and nutrients found in whole grains, which can help to reduce inflammation and promote good health. Whole grains contain beneficial nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, as well as fiber, which helps to slow down the absorption of carbohydrates and reduce inflammation in the body (20✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
7. Red Meat
There is some evidence to suggest that consuming red meat may be associated with an increased risk of inflammation. This is partly due to the fact that red meat is high in saturated fat, which has been shown to promote inflammation in the body (21✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
Additionally, red meat contains a molecule called Neu5Gc, which is not naturally produced by humans but can be incorporated into our cells and tissues when we consume red meat. The presence of Neu5Gc in our bodies has been shown to trigger an immune response and promote inflammation (22✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
Limited research on humans has also suggested that Neu5Gc may be a risk factor for colorectal cancer (23✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
8. Processed Corn
Corn is in so many products. You really need to be careful to avoid this one. There are a variety of corn derivatives like high-fructose corn syrup, corn starch, and corn oil. Eating corn in these refined forms spikes blood sugar and as we have seen above, spiked blood sugar leads to an increased insulin response, which creates a major inflammatory response.
Some experts suggest that consuming large amounts of corn oil, which is often used in processed foods and fast food, may contribute to inflammation due to its high omega-6 fatty acid content. While omega-6 fatty acids are important for good health, an excess of them in the diet can lead to inflammation (24✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
9. Artificial Chemicals and Additives
Anything artificially created, like chemicals and additives in foods, are not recognized by the body. They are foreign, and so naturally, the body needs to defend itself from these synthetic compounds, which means an inflammatory immune response.
One study published in the journal Nutrients found that a diet high in processed foods containing artificial additives was associated with higher levels of CRP, a marker of inflammation, in adults (25✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source. Additionally, some artificial sweeteners have been found to disrupt gut bacteria, which can also contribute to inflammation in the body (26✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
Another study published in the journal PLOS ONE found that exposure to a common food additive called titanium dioxide, which is used as a whitening agent in some processed foods, can induce low-grade inflammation and alter gut microbiota in mice. This inflammation was associated with changes in the expression of genes related to immune function and gut barrier integrity (27✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
A review of studies published in the journal Food and Chemical Toxicology found that consumption of food dyes, which are commonly used in processed foods to add color, can cause allergic reactions and may contribute to chronic inflammation in some individuals. The authors noted that more research is needed to fully understand the potential health effects of food dyes (28).
10. Trans Fats
Trans fats, also known as partially hydrogenated oils, are a type of unsaturated fat that have been chemically altered to improve the texture and shelf life of processed foods. However, numerous studies have linked the consumption of trans fats to inflammation and an increased risk of chronic diseases.
Here are a few studies that highlight the negative impact of trans fats on inflammation:
- A study published in the Journal of Nutrition found that a high intake of trans fats was associated with higher levels of markers of inflammation, including C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) in women (29✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
- Another study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that a diet high in trans fats was associated with increased levels of CRP in men (30✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
- A review of studies published in the journal Nutrients concluded that trans fats are pro-inflammatory and can contribute to the development of chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome (31✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
- A study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology found that replacing trans fats with healthy unsaturated fats, such as olive oil and nuts, can reduce inflammation and improve cardiovascular health (32✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
Given the negative impact of trans fats on inflammation and overall health, it’s important to limit your intake of processed foods and choose whole, unprocessed foods whenever possible.
Foods That Fight Inflammation
You can fight inflammation by slowly ditching the foods above, and incorporating the 10 foods below.
Remember that inflammation is also caused by stress, lack of sleep, pollution, smoking, and lack of exercise (as mentioned below), so it isn’t just about fixing a poor diet. Practice stress-reduction techniques, go to sleep earlier, quit smoking (if you do), and start walking if you’re not active.
1. Turmeric: one of the best anti-inflammatory foods out there. Its active ingredient, curcumin, inhibits the activity of COX-2 and 5-LOX, two enzymes involved in the inflammatory response (33✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source. Curcumin also blocks inflammatory pathways and prevents inflammatory proteins from triggering pain and swelling.
2. Blueberries: high in antioxidants, which prevent oxidative stress and inflammation. Reduce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines while increasing the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines (34✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
3. Dark Leafy Greens: kale, collards, spinach, romaine, you name it! Possess strong anti-inflammatory properties due to their high content of various nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals (35✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
4. Avocado: contain polyhydroxylated fatty alcohols (PFAs), monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs), and phytosterols, which provide our bodies with anti-inflammatory benefits (36✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
5. Watermelon: incredibly alkalizing, watermelon helps buffer the acid intake from a high-acid diet (namely, a high-inflammatory diet). Contains citrulline, lycopene, and vitamin C which all help reduce inflammation in the body (37✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
6. Hemp Seeds: have been found to have anti-inflammatory effects due to their high content of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, as well as their gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) content (38✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source. Hemp seeds are naturally anti-inflammatory, helping people suffering from inflammatory-related diseases.
7. Medicinal Mushrooms: medicinal mushrooms like shiitake, reishi, and turkey tail mushrooms contain high-molecular-weight polysaccharides (HMWP), which improve immune function and help battle inflammation (39✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
8. Ginger: like turmeric, ginger is a popular anti-inflammatory root. It contains compounds called gingerols and shogaols that have been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects on the body (40✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
9. Beets: high in antioxidants, beets help fight to repair cell damage caused by inflammation. They are also high in inflammation-fighting potassium and magnesium (41✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
10. Pineapple: contain the inflammation-fighting enzyme called bromelain. It helps regulate the immune response that often creates unwanted inflammation in the body (42✓)✓ Trusted ResourcePubMed CentralHighly respected database from the National Institutes of HealthRead source.
The Bottom Line
Inflammation is a natural response of the body to injury or infection, but chronic inflammation has been linked to many health problems, including heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
One of the ways we can help reduce inflammation in the body is by paying attention to the foods we eat. Some foods can trigger an inflammatory response, while others can help fight inflammation.
By incorporating more of these anti-inflammatory foods into your diet and reducing your intake of pro-inflammatory foods, you can help reduce inflammation in your body and improve your overall health.








Thank you Carley, very informative. I have fibromyalgia. 2020 is the year to break old eating habits & make choices in my life to rid stress. Would love to hear about your book in the coming year. ❤️
Hey Pauline – of course! If you sign up to my newsletter in the sidebar, homepage or footer, you’ll be the first to know! 🙂
I have a question. Corn is bad but what do I use as a snack if I can’t do bread or rye or oats or any wheat?
I sometimes just want a cracker bread or or toastie with some avo or hummus but if corn us bad are corn cakes also bad?
You could try rice cakes or quinoa cakes!